C# OpenCV 강좌 : 제 25강 - 직선 검출
직선 검출(Hough Transform Lines)

영상이나 이미지의 직선을 찾기 위해 사용합니다.
영상이나 이미지에서 HoughLines2를 이용해 직선을 찾을 수 있습니다.
원본(Source, src)은 영상이나 이미지를 사용합니다.
클래스 코드
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using OpenCvSharp;
namespace Project
{
class OpenCV : IDisposable
{
IplImage bin;
IplImage canny;
IplImage houline;
public IplImage Binary(IplImage src)
{
bin = new IplImage(src.Size, BitDepth.U8, 1);
Cv.CvtColor(src, bin, ColorConversion.RgbToGray);
Cv.Threshold(bin, bin, 120, 255, ThresholdType.Binary);
return bin;
}
public IplImage CannyEdge(IplImage src)
{
canny = new IplImage(src.Size, BitDepth.U8, 1);
Cv.Canny(src, canny, 50, 100);
return canny;
}
public IplImage HoughLines(IplImage src)
{
houline = new IplImage(src.Size, BitDepth.U8, 3);
canny = new IplImage(src.Size, BitDepth.U8, 1);
canny = this.CannyEdge(this.Binary(src));
Cv.CvtColor(canny, houline, ColorConversion.GrayToBgr);
CvMemStorage Storage = new CvMemStorage();
//Standard 방법
CvSeq lines = canny.HoughLines2(Storage, HoughLinesMethod.Standard, 1, Math.PI / 180, 50, 0, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < Math.Min(lines.Total, 3); i++)
{
CvLineSegmentPolar element = lines.GetSeqElem<CvLineSegmentPolar>(i).Value;
float r = element.Rho;
float theta = element.Theta;
double a = Math.Cos(theta);
double b = Math.Sin(theta);
double x0 = r * a;
double y0 = r * b;
int scale = src.Size.Width + src.Size.Height;
CvPoint pt1 = new CvPoint(Convert.ToInt32(x0 - scale * b), Convert.ToInt32(y0 + scale * a));
CvPoint pt2 = new CvPoint(Convert.ToInt32(x0 + scale * b), Convert.ToInt32(y0 - scale * a));
houline.Circle(new CvPoint((int)x0, (int)y0), 5, CvColor.Yellow, -1);
houline.Line(pt1, pt2, CvColor.Red, 1, LineType.AntiAlias);
}
//Probabilistic 방법
//CvSeq lines = canny.HoughLines2(Storage, HoughLinesMethod.Probabilistic, 1, Math.PI / 180, 140, 50, 10);
//for (int i = 0; i < lines.Total; i++)
//{
// CvLineSegmentPoint element = lines.GetSeqElem<CvLineSegmentPoint>(i).Value;
// houline.Line(element.P1, element.P2, CvColor.Yellow, 1, LineType.AntiAlias);
//}
return houline;
}
public void Dispose()
{
if (bin != null) Cv.ReleaseImage(bin);
if (canny != null) Cv.ReleaseImage(canny);
if (houline != null) Cv.ReleaseImage(houline);
}
}
}세부 코드
houline = new IplImage(src.Size, BitDepth.U8, 3);
canny = new IplImage(src.Size, BitDepth.U8, 1);
canny = this.CannyEdge(this.Binary(src));
Cv.CvtColor(canny, houline, ColorConversion.GrayToBgr);houline은 CannyEdge를 적용한 이미지에 Drawing을 색상을 하기 위해 3채널로 사용합니다.
즉, CannyEdge 위에 색상있는 Circle 또는 Line을 사용하기 위해 적용합니다.
계산을 위한 canny를 선언한 후, CannyEdge를 적용합니다.
CvMemStorage Storage = new CvMemStorage();
CvSeq lines = canny.HoughLines2(Storage, HoughLinesMethod.Standard, 1, Math.PI / 180, 50, 0, 0);직선(Lines)을 검출하기 위하여 Storage, lines를 선언하고 canny.HoughLines2()를 적용합니다.
canny를 계산을 위한 이미지로 사용햇기 때문에, 이 이미지에 HoughLines2()를 적용합니다. lines에 길이와 각도가 저장됩니다.
*.HoughLines2(메모리 저장소, 변환 방법, rho, theta, 임계값, 매개변수1, 매개변수2)입니다.
rho는 누산기의 거리 분해능입니다. theta는 누산기의 각도 분해능입니다. 단위는 라디안이므로 각도 단위로 입력합니다.
변환방법이 Standard이므로 매개변수의 값은 사용하지 않습니다.
- 변환방법
HoughLinesMethod.Standard: rho와 theta 반환HoughLinesMethod.Probabilistic: 시작점과 끝점 반환HoughLinesMethod.MultiScale: 고전적 Hough Transform 방법, rho와 theta 반환
- 매개변수
매개변수1Standard 사용 시: 사용 안함Probabilistic 사용 시: 최소 선 길이MultiScale 사용 시: rho에 대한 약수
매개변수2Standard 사용 시: 사용 안함Probabilistic 사용 시: 최대 선 간격MultiScale 사용 시: theta에 대한 약수
Standard Code
for (int i = 0; i < Math.Min(lines.Total, 3); i++)
{
CvLineSegmentPolar element = lines.GetSeqElem<CvLineSegmentPolar>(i).Value;
float r = element.Rho;
float theta = element.Theta;
double a = Math.Cos(theta);
double b = Math.Sin(theta);
double x0 = r * a;
double y0 = r * b;
int scale = src.Size.Width + src.Size.Height;
CvPoint pt1 = new CvPoint(Convert.ToInt32(x0 - scale * b), Convert.ToInt32(y0 + scale * a));
CvPoint pt2 = new CvPoint(Convert.ToInt32(x0 + scale * b), Convert.ToInt32(y0 - scale * a));
houline.Circle(new CvPoint((int)x0, (int)y0), 5, CvColor.Yellow, -1);
houline.Line(pt1, pt2, CvColor.Red, 1, LineType.AntiAlias);
}for문과 Math.Min(lines.Total, 3)은 lines의 값이 3보다 낮은 값만 사용하게끔 하여 반복합니다.
Math.Min()에서 3보다 높아질 경우, 더 많은 선들을 검출합니다.
element를 선언하고, 검출된 선의 거리와 각도를 가져옵니다.
먼저, HoughLines의 검출 방법은 모든 점들을 직선의 방정식을 만듭니다.
이 직선의 방정식이 교차하는 점이 가장 많은 점을 기준으로 직선으로 판별합니다. 이 방법을 기준으로 선을 검출합니다.
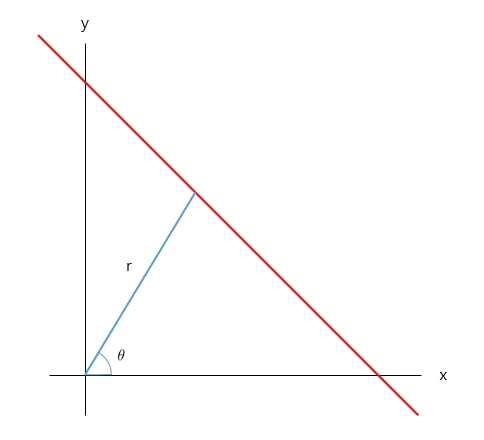
검출된 선의 그래프는 위와 같습니다.
거리(r)는 element.Rho을 의미하며, 각도(theta)는 element.Theta를 의미합니다.
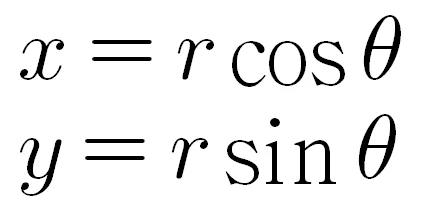
좌표를 찾기 위하여 수식을 만듭니다. x와 y는 위와 같습니다.
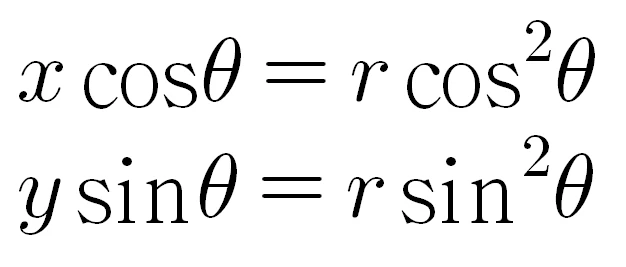
양변에 각각 cosΘ와 sinΘ 곱합니다.
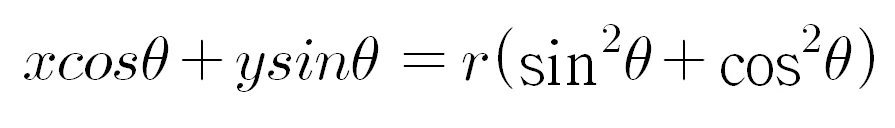
두 식을 더하여 r에 대해 정리합니다.
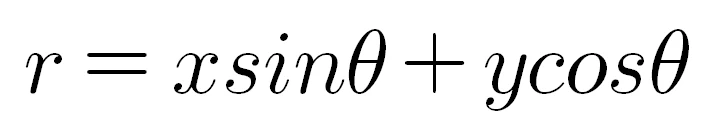
r에 대한 함수는 위와 같이 얻을 수 있습니다.
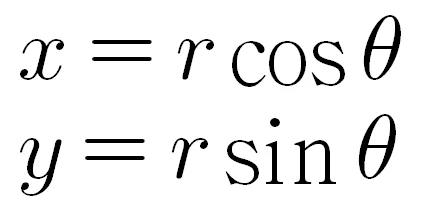
x0와 y0는 위 식을 사용합니다.
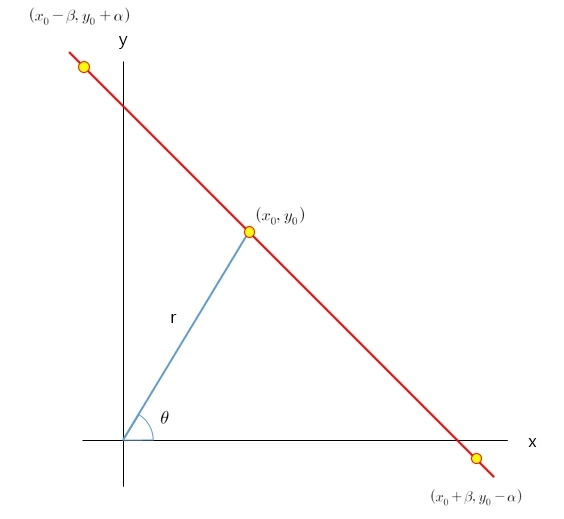
x0와 y0는 위 그래프의 지점에 위치하며 이에 따른 직선을 그리기 위하여 scale 만큼 범위를 띄웁니다.
scale은 적절한 값으로 조정하시면됩니다.
위와 같이 pt1과 pt2를 구해진 지점에서 각도와 스케일을 이용하여 검출된 직선을 표시할 수 있습니다.
검출된 지점은 결과에서 노란원으로 확인할 수 있습니다.
Probabilistic Code
for (int i = 0; i < lines.Total; i++)
{
CvLineSegmentPoint element = lines.GetSeqElem<CvLineSegmentPoint>(i).Value;
houline.Line(element.P1, element.P2, CvColor.Yellow, 1, LineType.AntiAlias);
}CvLineSegmentPoint 형식의 element를 선언하고, 검출된 선의 시작점과 도착점을 가져옵니다.
시작점은 P1을 의미하며, 도착점은 P2를 의미합니다.
출력 결과
Standard

Probabilistic

공유하기
 Kakao
Kakao
 Naver
Twitter
LinkedIn
Facebook
Naver
Twitter
LinkedIn
Facebook
댓글 남기기